In November 2024, Ethereum researcher Justin Drake introduced the “Beam Chain” proposal at Devcon Bangkok, aiming to modernize Ethereum’s consensus layer by integrating advanced cryptographic techniques and addressing current inefficiencies.

Understanding Beam Chain
The Beam Chain proposal seeks to overhaul Ethereum’s consensus mechanism, focusing on three primary areas:
- Block Production: The proposal aims to decentralize the builder and relay levels, enhancing censorship resistance. It also suggests reducing slot times to four seconds, enabling faster block generation and quicker transaction finality.
- Staking Structure: A significant change involves lowering the minimum ETH required to become a validator from the current 32 ETH to just 1 ETH. This reduction is intended to make staking more accessible, promoting greater network participation and decentralization.
- Cryptographic Enhancements: The integration of SNARK-based, post-quantum cryptography using hash-based signatures is proposed to ensure Ethereum’s resilience against future quantum computing threats. This approach would enable real-time consensus proofs on standard hardware, bolstering security.
Justin Drake’s Vision
Drake envisions leveraging recent advancements in cryptography, particularly zero-knowledge proofs (SNARKs), to enhance Ethereum’s performance and security. By “SNARKifying” Ethereum’s state transition function, the network could achieve faster slot times and single-slot finality, reducing transaction wait times and eliminating certain types of value extraction from transactions.
Potential Impact on Ethereum’s Price
Price Implications: The Beam Chain proposal is still in the research phase, and its potential impact on Ethereum’s price remains speculative. If implemented successfully, the enhancements could bolster investor confidence, potentially leading to positive price movements. However, the extended timeline and inherent risks associated with such a significant overhaul may also introduce uncertainty, which could affect market sentiment.
Transaction Fees: While the Beam Chain aims to improve block production efficiency and reduce slot times, its direct impact on transaction fees is not explicitly outlined. Enhanced efficiency could lead to increased transaction throughput, which might help alleviate network congestion and, in turn, reduce gas fees. However, other factors, such as overall network demand and Layer 2 scaling solutions, will continue to play significant roles in determining transaction costs.
Challenges and Considerations
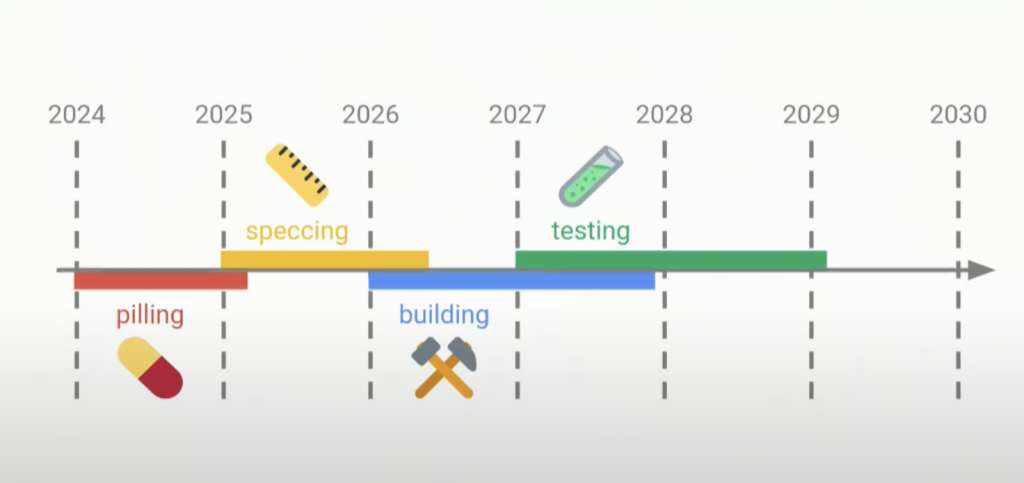
Implementing the Beam Chain involves significant technical challenges, including the integration of advanced cryptographic methods and substantial changes to Ethereum’s consensus architecture. The proposed timeline reflects the complexities of making major changes to the world’s second-largest blockchain, emphasizing the need for extensive research, development, and testing to ensure network security and stability.
In summary, the Beam Chain proposal represents a forward-looking vision for Ethereum’s evolution, aiming to enhance performance, security, and decentralization. As the proposal progresses through research and development, its potential impacts on Ethereum’s ecosystem will become clearer, offering insights into the future trajectory of the network.
Suggested Release Date
As of now, the Beam Chain proposal is in its early stages, with a comprehensive roadmap yet to be finalized. Considering the complexity of the proposed changes and the need for thorough testing and community consensus, a tentative release date is projected around 2029. This timeline aligns with the cautious approach necessary for implementing substantial modifications to Ethereum’s consensus layer.
In summary, while the Beam Chain proposal represents a significant advancement for Ethereum, its potential effects on price and transaction fees will depend on successful development, community acceptance, and broader market dynamics over the coming years.